OWW AWES Applied to HG Launching
One-Way Wings Airborne Wind Energy System
-- method being explored--
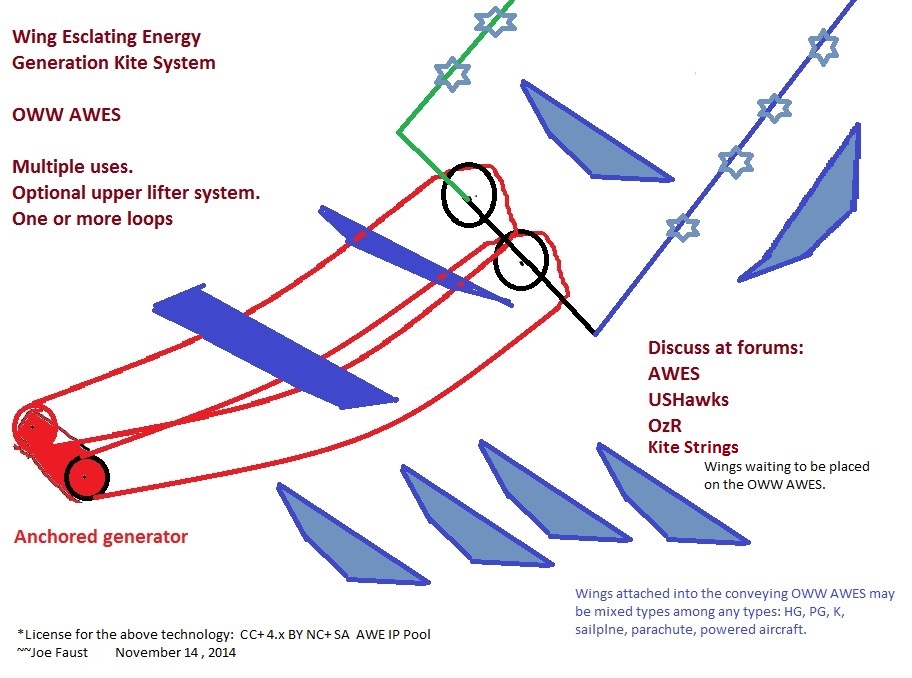
The following introduces a novel family of tethered-airfoil kite-system AWES that use loop tethers (one or more) and a series of wings that detach at the far downwind point of the loops (one or more); a brief look and one might think that one is seeing a conventional laddermill; but no, the following family of AWES distinctly entirely detach involved wings into free-flight; the return loop half of the AWES has no wings. Only the outgoing half of the loop set have working wings. The wings of these AWES are denoted as OWWs standing for "One-Way Wings." One such wing would be denoted as OWW. Plural: with the "s." Note: An AWES in this special family may or may not use severe lifting kite system in addition to the basic OWWs that are kited on the loop or loops; severe lifting upper kite system would allow different designs of OWWs for effecting generation of electricity. Note: The OWW AWES family differs from Selsam, Ockels, Bolonkin, and others, as those other systems keep the wings attached to the AWES. The novel emphasis on detaching the wings (thus OWW name) provides some potential advantages depending on the specific design. An AWES OWW system may fly one or more than one OWW; there could be hundreds of attached OWWs on the loop set, e.g. Notice that groundgen shaft turns in just one direction. One may replace the electrical groundgen with other devices for doing practical works.
One-way wings (OWW, OWWs) fly finally downwind, perhaps following fancy paths (but need not) while driving a groundgen; but then at the far downwind lofty point at the far-from-system-anchor-set top of the driven loop set (one or more loops holding the OWWs) the OWWs deliberately leave the operating AWES. The OWWs will have completed their lifting and dragging of the loop set of the AWES; then the OWWs will deliberately detach from the AWES loop set; the OWWs will go into free-flight without immediate further interaction with the AWES parts.
Then depending on the wings' designs, those OWWs will have some kind of next play depending on purposes. Here are some purposes of AWES OWWs upon their detaching from the AWES flight system at the far end of a set of loops (one or more):
•Give free-flight experience to humans who may have been mounted in the OWWs. The experience may be of different sorts:
•Hang gliding (adventure, sport, commerce, personnel placement into activities, science, competition, recreation, ...)
•Paragliding (see similar purposes in above line)
•Sailplane flying ( see above for similar purposes)
•The OWWs in free-flight might be so designed to glide all the way back to the AWES' anchor place for attaching to the loop set for another working session for the AWES generation purpose.
•The OWWs in free-flight migh have goods that would soar to far points for delivery of the goods. Such OWWs might be used just once or recycled for further services. Some OWWs might be programmed to self-destruct after fulfilling an objective.
•The OWWs in free-flight might have RATs that might work during gliding or fall in order to give energy for on board duty or duty after landing. One after-landing duty might be morphing itself and driving itself back to the AWES anchor for another AWES service cycle.
•The OWWs in free-flight might land soon at far points and collected for a group return to the AWES anchor area for another service cycle on the AWES loop set. OWWs will be ending their life soon after detaching from the AWES loop set. For instance, some OWWs might be designed to detach and fly (or drop, a kind of flight) into a pool of hot lava, into an corrosive chemical pool, into a forest fire, or the like. Or the wing might be of such design that the materials of the wing would be used for food, fertilizer, making other things, ... The OWWs might be carrying water or fire retardant or practical explosives for practical peaceful purposes.
• Those skilled in the arts will find other uses of the AWES OWW method.
AWES OWW systems may farm laterally, windwardly, or also vertically (stacking). They may also be based on massive kite arches or kite domes. The mechanics involve and method may be adopted to a media different from air, e.g., water or solar radiation, etc. OWWs may be very soft or any gradation of stiffness to fully rigid. OWWs may be LTA or HTA or have a mix of types of wings in one AWES. For the OWW AWES that keeps using detached OWWs for further generation flight, the OWWs may be attached again to the working loops in various ways which need not be rehearsed herein, but would be known by those skilled in the arts.
*License for the above technology: CC+ 4.x BY NC+ SA AWE IP Pool Use personally, but when using commercially, negotiate with kPower, Inc. regarding thresholds and fair respects.
The OWW AWES family is dedicated to all the people who have come into my life but detached in some way to have further play; thanks for generating blessings while attached to my loopy life; may your free-flight further bless you and others.
~~JoeF
The president of the USHawks has given a first-order effort at illustrating part of the essence of one embodiment of an OWW AWES:
Scroll one message down from the first post:
US Hawks Hang Gliding Association • View topic - OWW HG Launch Escalator AWES
==============
The OWW AWES is primarily an energy producer method with very many secondary applications, one of which is to launch scores of hang gliders quickly off flatland. A primary operation mode is continuous energy production. Wind is needed for the kite strings to do their job.
~JoeF